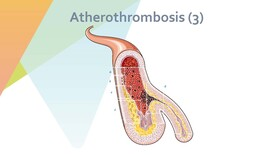
Nursing and Prevention of Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a chronic condition that can lead to severe cardiovascular complications. Effective nursing care and preventive strategies are essential for managing risk factors and promoting vascular health.
Key Points
- Prevention of atherosclerosis begins with lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet and regular physical activity.
- Nursing care focuses on empowering patients to take an active role in their treatment.
- Early preventive measures, even in childhood, can significantly reduce the risk of developing atherosclerosis.
Nursing Care Strategies
Patient Empowerment
- Encourage patients to take initiative and actively cooperate with treatment plans.
- Provide education on the importance of lifestyle changes and adherence to medical advice.
Dietary Recommendations
- Calorie control:
- Avoid excessive calorie intake to maintain a normal weight.
- Prevent weight gain, especially in individuals over 40 years old.
- Low-fat, low-cholesterol diet:
- Limit fat intake to no more than 30% of total calories, with no more than 10% from animal fat.
- Restrict cholesterol intake to no more than 500 mg per day.
- Reduce consumption of sucrose and sugary foods.
- Avoid saturated fats:
- Minimize intake of animal fats and vegetable oils high in saturated fatty acids.
- Promote a light diet:
- Include foods rich in vitamins and plant proteins.
- Avoid overeating to reduce the risk of angina pectoris and myocardial infarction in patients with coronary atherosclerosis.
Physical Activity
- Benefits:
- Prevents obesity, strengthens the circulatory system, and regulates blood lipid metabolism.
- Guidelines:
- Tailor physical activity to individual physical condition, habits, and heart function.
- Start gradually and avoid strenuous activity.
- Recommended activities:
- Walking (one hour daily, split into several sessions).
- Health exercises and Tai Chi, especially for elderly individuals.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Maintain a regular lifestyle with a balanced work-life schedule.
- Foster an optimistic and cheerful mood to reduce stress.
- Avoid overwork and emotional agitation.
- Ensure adequate sleep and rest.
Smoking and Alcohol
- Smoking:
- Strongly discouraged due to its adverse effects on vascular health.
- Alcohol:
- Avoid strong alcohol; small amounts of low-concentration alcohol may increase HDL cholesterol but are not recommended for long-term use.
Management of Related Conditions
- Actively treat conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and obesity.
- Addressing these conditions can significantly reduce the risk of atherosclerosis progression.
Early Prevention in Childhood
- Encourage children to avoid diets high in cholesterol and animal fats.
- Prevent overeating to avoid weight gain and reduce long-term cardiovascular risk.
Challenges and Future Directions
- Challenges:
- Encouraging long-term adherence to preventive measures.
- Addressing barriers to lifestyle changes in diverse populations.
- Future directions:
- Development of community-based programs to promote cardiovascular health.
- Advances in personalized prevention strategies based on genetic and lifestyle factors.
Patient and Public Education
- Raise awareness of the importance of early prevention and lifestyle modifications.
- Provide resources and support for adopting heart-healthy habits.
- Highlight the role of nursing care in managing and preventing atherosclerosis.
Nursing and prevention strategies play a vital role in reducing the burden of atherosclerosis. By adopting a proactive approach to lifestyle changes and risk factor management, individuals can significantly improve their cardiovascular health and quality of life.